
Contract
2.1 Applicable laws
1. Legislative Branch~> Law
(= Congress) 입법부에서
2. Common Law
1) Service
2) Real property(land, building)
3. ACI
단체에서 협의한 법, State에서 adopts
Uniform Commercial Code2
1) tangible good
>> 종류가 섞여있다면 비중이 큰걸 택한다
2.2 Basic concept of contract

2. Acceptance: mutual assent
3. Consideration of both OR & EE
= bargain for exchanged
= Legal detriment 손실, 손해
ex) a. Promise_promise
b. Cash
c. Property
d. Forbearance(안하기로약속)
- must have a legal detriment
- must be legally sufficient(금액은 상관없음)
2.3 Type of Contracts
1. Bilateral K (Promise <-> Promise)
2. Unilateral K (Action, right now <-> Promise)
우리 뽀삐를 찾아주시면 사례금 50만원
3. Executory K(signed offer, Not fully performed)
4. Executed K (fully performed)
5. invalid(void, voidable) vs Valid
| Valid | Valid: a contract that has been legally formed and enforceable |
| Invalid | Void: no contract is ever created - violation of public policy, illegal conduct, 마약거래 - Duress: physical forces, 때려서 강제함 - Incompetent party 정신적 지체인 경우 |
| Voidable: a valid contract that can be set aside(취소) - Minor as a party - Mutual, unilateral mistake |
6) Quasi K (준계약, 계약x) vs implied in law contract
| Quasi-contract: contract is unenforceable, legal remedy available ex) Unjust enrichment |
| Implied-in-law contract: not satisfied the contractual requirements, but enforceable because of public policy ex) saving other's life |
2.4 Offer
1. ways to offer-writing, oral, action
2. Intent of offeror + recognition of the intent by offeree
offeree's recognition: EE가 상황을 인지할수있는가?
Offer is effective when offeree receives (도달주의)
3. Statement ≠ offer
- Invitation to treat = Advertisement (* targeting customer가 있는 경우 offer, ex. 첫등록고객 50%off)
- Opinion (ex. professional opinion about a medical issue)
- Inquiry
4. Requirements of offer
| Common law | UCC2 | |
| Item | Service Real property |
Tangible goods |
| Party | O | O |
| Quantity | O | O |
| Price | O | X(open price term) |
| subject matter | O | O |
| Time of performance | O | O |
- tems must be definite and certain under common law
- Open price term: at the time of delivery 2) at the time the party breaches the contract
2.5 Termination of offer
1. Basic rule
- Offer can be revoked before acceptance
- Offer is terminated, when the offerEE receives the revocation/ offerOR receives the EE's counter offer
2. Revocation
- OR revoke or bring back the offer
- EE recognized the revoked offer* 인지함!
3. Rejection
- EE's rejection
- EE's counter offer(new offer, different from the original offer)
* inquiry is not a counter offer(will you sell for $90?)
4. Lapse of time (Open 기간 경과)
* Consideration 없는 기간과 방법은 강제력이 없음, revocation 가능
5. Operation by law
Death of insanity of offeror/offeree
6. Option Contract ( 기간 조건을 명시한 offer, stipulated rule)
consideration(o): irrevocable before the end of the period,
even if the offeree rejects or provides a counteroffer, the option contract is still available
2.6 Firm offer(UCC2, Tangible goods)
1. Requirements
- UCC2 (sale of tangible goods)
- Offeror is a merchant
- written offer, signed by defendant 피고(상인)
- Irrevocable period (not mentioned, mentioned but more than 3M >3M)
- Consideration X (but same with option K with consideration)
2. Battle of form
| Merchant - Merchant | Merchant - non merchant | |
| Material terms | part of contract(x) | part of contract(x) |
| Immaterial terms | Part of contract(o)+no rejection within reasonable time | part of contract(x) |
| agreed provisions | Part of contract(o) | Part of contract(o) |
2.7 Acceptance
1. General
- Offeree must know about the offer in order to accept
- only by offeror accepts the offer
- The acceptance is valid when the offeree complies with the stipulated rules in the offer
- Silence is not acceptance
| Common law Mirror image rule(o) (offer=acceptance) |
UCC2 Mirror image rule (x) (offer ≠ acceptance) 똑같지 않아도 됨 |
2. Bilateral contract in option K (Promise - promise)
- Writing, oral, conduct > Offeror must receive the acceptance according to the offer
- Time of acceptance = at the time the offeror receives the acceptance
3. Mailbox rule without option K(발송주의)
- not option K
- Time of acceptance = at the time the offerEE sents the acceptance
| A->B 1) offer $1K (3.1.19) 2) Accept mail sent (3.5.19) K체결 3) revocation (3.8.19) 4) Letter arrived (3.11.19) |
A->B 1) offer $1K (3.1.19) 2) rejection (3.2.19) on transit 3) Accept (3.3.19) on transit 4) Accetptance arrives first (3.5.19) Rejection second (3.6.19) |
4. Unilateral contract (performance - promise)
- until the performance is done > acceptance x, option K o
- Time of acceptance = at the time the offeree fully provides the performance according to the offer
- EE must acknowledge the offer and rely on the offer before changing his/her position
| 1) A가 Notice를 좀_option K with consideration 2) 개를 찾으러 감_substantial change in action 3) 개 찾음 4) B에게가서 사례금 요구_K formed 5) B는 사례금을 줘야함 |
1) A가 개 발견 2) 이름표를 보고 B에게 찾아줌 3) Notice 발견 4) B에게가서 사례금 요구 5) B는 사례금을 줄 필요없음 |
5. UCC2 = sales of tangible goods
- Common law, mirror image rule, offer=acceptance, enforceable agreement
- Battle of form
- Shipment without sending acceptance
1) shipping conforming goods,
at the time of the shipment > acceptance = enforceable contract = executed contract
2) shipping non-conforming goods
at the time of the shipment > acceptance = enforceable contract > breach of contract
3) shipping non-conforming goods + accommodation (핑계)
at the time of the shipment > counter offer > breach of contract (x)
| Items | Common law | UCC2 |
| Objective | Intangible personal property real property service |
tangible personal property |
| option contract & firm offer |
option contract | option contract firm offer |
| Time of acceptance | stipulated rule mailbox rule |
stipulated rule mailbox rule |
| How to accept | mirror image rule * unequivocal and unconditional definite and certain * price, quantity, description performance |
battle of form * additional term: valid * bet non-merchant: proposal * bet merchant: part of the contract unless 1) preclude 2)materially alter 3)objection open terms except quantity *open price, opentime of payment |
| Modificaiton of contract | need new consideration | no need new consideration |
| Statute of fraud (written K) |
1-year rule sale of real property suretyship or guaranty sale of intangible personal property over $5K |
sale of tangible personal property $500/more |
2.8 Other Issues
1. Promissory estoppel
- no contract, no consideration, yes enforcement
- Requirements
promise, substantial reliance on the promise
the reliance which is reasonable and foreseeable + damages
protecting for the justice
| 아버지, 자녀결혼 1) APT promise 2) stop searching apt, buy an appliance 3) Father "I am sorry" 4) enforceable= promissory element 1) rely on father's promise 2) reliance is reasonable 3) Damage |
2. Promise for charity donation
lack of consideration > enforceable contract
3. Auction
- auction with reserve/without reserve
4. Condition precedent 선제조건
- agreement is enforceable after the satisfaction of the condition precedent
- oral, written 상관없음>> if my wife permits
5. Condition subsequent
2.9 Modification
1. Common law
- like a new contract
- new considerations necessary
2. UCC2
- Good faith is sufficient
- consideration is unnecessary
2.10 Defense -> Unenforceable agreement
1. Post consideration
Not bargained for exchange
exception-moral consideration
2. Gift > unenforceable contract
3. Preexisting duty rule
- Party is already obligated to do something, and promises to do the exact same thing
- Debt case
| a $10K oral agreement b Dispute *dispute 있으면 기존거래 인정 X Debtor 5K loan, 진심으로 5K라고 생각한다면 Creditor 10K loan c 10K signed, Debtor에게는 손해인 상황이다. 따라서 consideration이 있다고 볼수있다. |
4. Minor as a party

5. Incompetent party

6. Illegal transaction
- criminal conduct, cannot be a consideration
- Service already performed without the proper license
| Lawer, CPA 등등>> 고객을 보호하기위함 License 없이 행위한것에 대해 대가를 받을 수 없음 |
어업권, 사냥 허가권>> State Rev Seeking License 없이 행위한것이라도 대가를 주어야함 |
- Violation of public policy
a.unreasonable restraint of transactions -> voidable contract
b.restriciton of reasonable time and reasonable district are good for protecting a party in a certain manner
c.exceptions: sale of business 사업양도
7. Unconscionability
- 어느 한쪽에 완전히 부당한 경우
- 의사-환자, 변호사-고객
8. Impossibility ≓ impracticability
9. Misrepresentation
Negligent misrepresentation
Intentional misrepresentation = Fraud
Reckless disregard for truth =Fraud
Result
Mistake > Negligent > Gross negligence > Reckless disregard
10. Mistake (claim가능)
1) Mutual mistake
- voidable contract by either party
- reformation-remedies
2) Unilateral mistake
- only one of the parties knew or should have known
- voidable contract by an innocent party
11. Duress
- Physical threat of violence -> void contract
- Economic threat -> voidable contract if one party threatens to ruins the other party's biz
12. Undue influence
- vulnerability of the victim
- Apparent authority of the wrongdoer
- Actions and tactics of the wrongdoer
- Anenequitable result
13. Statute of limitation(SOL)
소멸시효, SOL 기간이 지나면 더 이상 소송할 수 없음
computed from the date of the breach of the contract
2.11 Statute of Fraud
- The agreement must be reduced in "writing"+"Internet"
- Signed by a defendant if not, the agreement is unenforceable
- It needs not to be in a single document
Type
1) Premarital agreement
Property allocation =enforceable, child custody child support ≠ enforceable
2) Real property transaction
lease(more than 1 yr), Sales of land, easement, mortgage
* exception:
- 2/3: partial payment, actual possession/dwelling, a substantial improvement on the land
- Lease contract less than 1year
3) Service contract more than 1year
4) Suretlyship(guaranty) agreement 보증계약
- debtor falls in default > surety pays the debt
- primary promise: debtor > secondary promise: surety
* corporation's int = president's int
5) UCC contract ≥ $500
- tangible good
* exception: a. specially manufactured good
b.confirmation letter
c. buyer received the good and paid in full
Confirmation letter
- after oral agreement > unenforceable contract
- a party sends a confirmation letter of an oral contract > enforceable contract
| Type | SOF | Exception | |
| 1 | Premarital agreement | O | |
| 2 | Real property transaction | O | - Partial payment - Actual possession - Substantial improvement on the land |
| 3 | Service contract more than 1yr | O | fulfillment of the oral contract |
| 4 | Suretyship(guaranty) agreement | O | Debtor's benefit = surety/guaranty's benefit |
| 5 | UCC contract more than or equal to $500 | O | - specially manufactured - confirmation letter - buyer received the goods and paid in full |
2.12 Parol Evidence Rule (PER)
- Trigger provision in a written contract("all-inclusive", "finally completed", "fully integrated")
- Previous evidence is not admissible to prove the truth
지금 계약서가 최종임/ 과거있던 모든자료 무시
* Exception
1) condition precedent 선제조건 " 과거자료 사용하겠다"
2) Parties capability/ability
3) K's terms are ambiguous
2.13 Assignment and Delegation

1. Assignment=tranasfer of right
- Assignor -> Right -> Assignee
- assignment extinguishes the assignor's right
- partial assignment is effective
- not need consideration for an assignment contract
- Any form of assignment contract is good(oral, conduct, writing)
2. Delegation=transfer of obligation
- Delegator -> Duty -> Delegatee (Delegator = Delegatee)
- no delegation extinguishes the delegator's duty, the Delegator is liable for the delegatee's conduct
- Partial delegation is effective
- not need consideration for an assignment contract
- Any form of assignment contract is good(oral, conduct, writing)
* Exception for delegation
* specially ordered contact(personal service, goods)
* substantial change of risk: requirement/output contract
* contract containing an exculpatory clause or assignment/delegation prohibition clause
* insurance assignment = assignment of beneficiary's right is prohibited
| Assignment | Delegation | |
| Subject | Transfer of right | Transfer of obligation |
| After the event | - assignor's right(x) - assignee's right(o) |
- Delegator's duty(o) - Delegatee's duty(0) |
| Exception | - specially ordered contract(service, goods) - Substantial risk change - contract terms |
3. Assumption in mortgage case
1) 부동산 구입시 은행대출을 받음 mortgagor = debtor, Mortagagee=creditor(은행)
2) Debtor가 Successor에게 자신의 title을 넘김
3) Successor가 mortagage를 assumption한 경우, 빛을 갚아야함
4) Defalut > 경매에 넘어감
5) 경매넘어가도 못갚으면, personal liabilty >가산을 털어 갚아야함
6) 그래도 successor가 못갚으면 > Debtor에게 personaly liabilty 생김
4. Vicarious liability > Respondeat superior
- 대리책임, A가 B에게 권한을 주었다면, 그 권한 내에서 발생한 사건은 A가 책임져야함
- Plaintiff(victim) can sue either a tortfeasor(empolyee) and an employer
if tortfeasor negligently conduced within the scope of employment
- Breach of contract + Negligence

2.14 3rd Party beneficiary contract
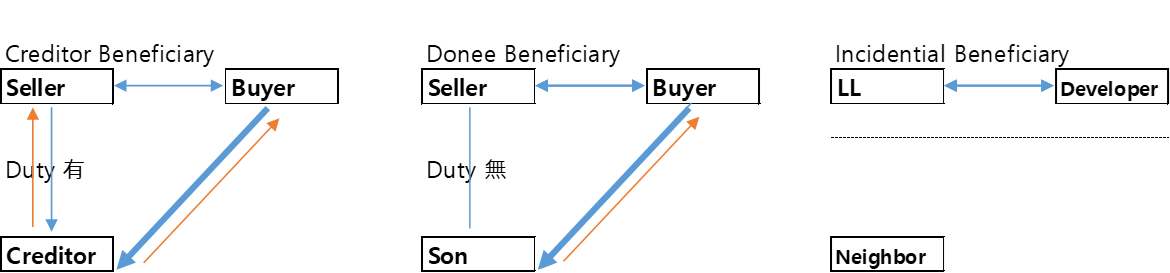
1. Intended 3rd party beneficiary
1) Creditor beneficiary
- seller, creditor -> enforceable contract
- seller, buyer -> enforceable contract
> Creditor has right to get paid from seller and buyer
2) Donee beneficiary
- Father, son -> Promise + motive to do so, no binding duties
- Father, LL -> enforceable contract
> Son claims to LL only
2. Incidental 3rd party beneficiary
3) Incidental Beneficiary
- LL, Neighbor -> Promise(x) + motive to do so(x)
- LL, Developer -> enforceable contract
> Neighbor has no right
2.15 Performance of Contract
- Perfect tender rule: seller must supply the buyer with goods that conform perfectly to the buyer's demands according to the contract
* Doctrine of substantial performance, substantial performance has been rendered
2.16 Title and Risk of Loss
1. INCOTERMS 2010
DAP: Delivered at a place
FOB: Free on Board
2. UCC2- common carrier
| 1) Shipment contract(FOB seller's place) seller에게 유리 shipping 하자마자 Title+ risk of loss > buyer에게로 |
2) Destination contract(FOB buyer's place) title+ risk of loss, shipping해도 seller에게 |
* Breach of contract 발생하면, 잘못한 쪽에게 불리하게 Risk of loss가 넘어감. Title도 불리하게 작용함
* Common carrier bailee is not liable for acts of god, acts of the shipper, or acts of a public enemy
3. Non-common carrier
| Seller = Merchant Seller must deliver the conforming goods to the buyer's hand Good tender of delivery by seller, Risk of loss > Buyer |
Seller ≠ Merchant Seller gives the notice to the buyer > reasonable tender Good tender of delivery by seller, Risk of loss > Buyer |
4. Ttile Issue
Bona fide purchaser
- "without notice" 선의의 구매자 보호
| 1) $500(1.3.19) > $550(1.12.19) 갚아야함 2) 전당포 친구 "~시계팔아", $700 Accept K 시계 넘김(1.5.19) 3) Client $550 (1.12.19) 시계 돌려줘 |
|
| Notice(0), Client's 전당포 친구는 고객의 시계인것을 알고 있었다. |
Notice(x), 전당포친구의 것 친구는 고객이 시계의 주인임을 몰랐다. 선의의 구매자 |
Identification of title
Identification = designated, segregated, labeled
Identification > risk of loss, title > buyer
After the trial period/sale or return contract
Risk of loss 뿐만 아니라 Title까지 사용자에게 넘어감. 물건 사용중에는 Seller가 risk of loss와 title 가지고 있음
2.17 Breach or Discharge of Contract
1. Breach of contract, shipping non-conforming goods
Non-breaching party's options
1) accept all goods 2) reject all goods 3) accept some goods and reject 4) selling,non-confirming goods(판매자회수거부)
2. Anticipatory repudiation / Adequate assurance(예상된 거부)
Anticipatory
1) 1.1.22 K-used cars, 10 units, $50K, Delivery(5.1.22), Signed
2) 3.1.22 Seller 마음변함, We are not selling-> Buyer Note (3.2.22)
3) buyer's option
a.기다린다, 거부가예상됨 b.소송 c.새로운업체+소송
Adequate assurance

Buyer AA(0) -> K성사
Buyer AA(x) -> Breach of K
3. Discharge of contract
Mutual rescission: 합의보고 계약취소함, discharge of K
Accord and satisfaction: Both parties agree to accept something in the settlement
Novation: 삼자합의를 본 변경
2.18 Remedies
1. Statute of limitation(SOL) 공소시효
- SOL limits the lawsuit
- SOL starts from the time of breach of contract
- UCC SOL 4yrs * may reduce 1yr, if both parties agree
2. Basic concepts
Breach of contract
- Monetary damage vs Specific performance
Quasi-contract, non-enforceable agreement
- Restitution
3. specific performance 이미있는 특수물건
- inapplicable to a service contract
- applicable to a contract of unique, special manufactured good(ex. real property, specially ordered goods
4. Monetary damages
1) Actual Damage = Compensatory damage
- Expected profit = liquidated damage
- [ K price - MKT price(breach한 날의 가격) ]
* 보증금(예약금)-> 기대이익 만큼 받음, 계약파기해도 이거 받고 소송 안할게
2) Incidental Damage, non breaching party가 계약의 피해를 줄이기 위해 쓴돈
ex) 다른 계약상대 알아봄
3) Consequential Damage 계약파기에 따른 피해금액, 단, breaching party가 해당내용에 대해 알고 있어야함
5. Punitive damage 징벌적 손해배상
- allowed in fraud, bad faith( 증명하기 어려움 )cases
6. Other issues
Arbitration, mediation, Reformation, injunction, recession
'회계 세무 공부 > AICPA 공부 요약' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [REG] Agency (0) | 2024.06.10 |
|---|---|
| [REG] Debtors, Creditors, Guarantors (0) | 2024.06.09 |
| [REG] Exempt organizations (0) | 2024.06.04 |
| [REG] Gift taxation and Trusts (0) | 2024.06.04 |
| [REG] S Corporations (0) | 2024.05.31 |




댓글